![]()
![]()
German Settlements in the east or Russia turns to west
Introduction - Germans in Russian cities
In the End of the 17th Century Russian's interest increased to Europe. The demand of foreign, especially German specialists, increased suddenly. That was the beginning of a German population in Russian cities. The settlement policy in the Russian Empire was strongly influenced by wars and revolutions. Even if German and Russian settlements nowhere borders directly, there were contacts between these two nations since Middle Ages.
The first Germans who went to Russia, was around the year 1200, at the time of Kievan' Rus1.
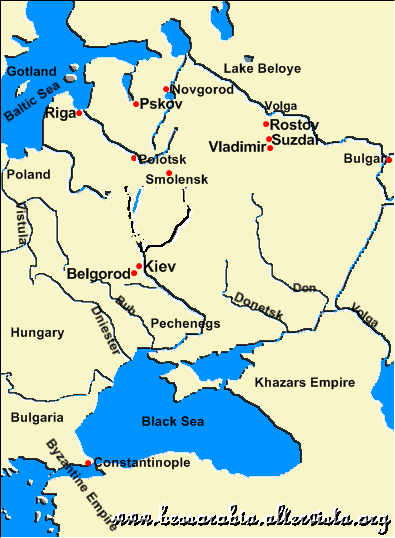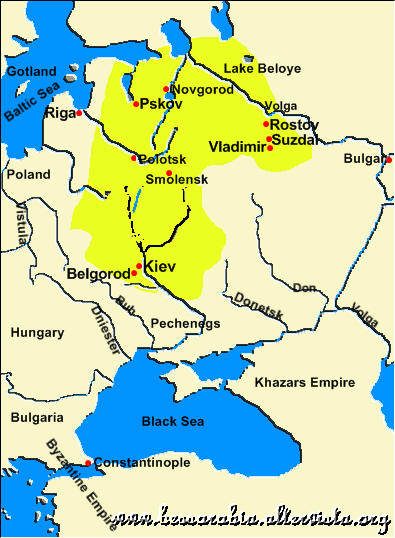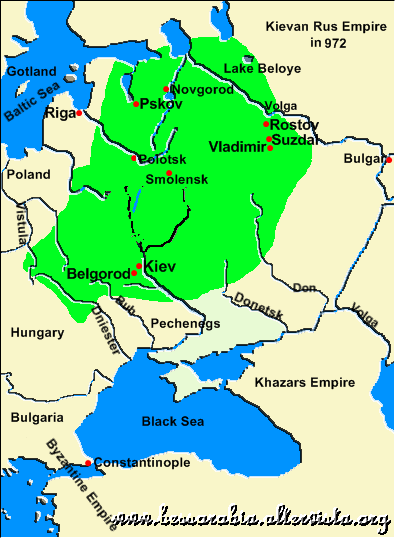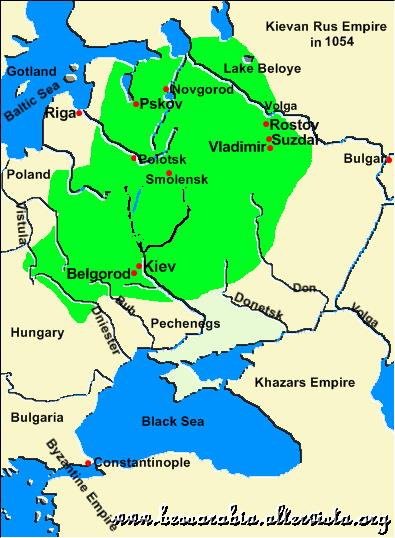
Kievan' Rus around 1000 AD
Later there were contacts between the Hanseatic League2 and the Russian cities of Pskov (German: Pleskau), Polack (Polotsk) and Veliky Novgorod where the Hanseatic Kontor Peterhof was opened, a first permanent German settlement in the Russians Empire.
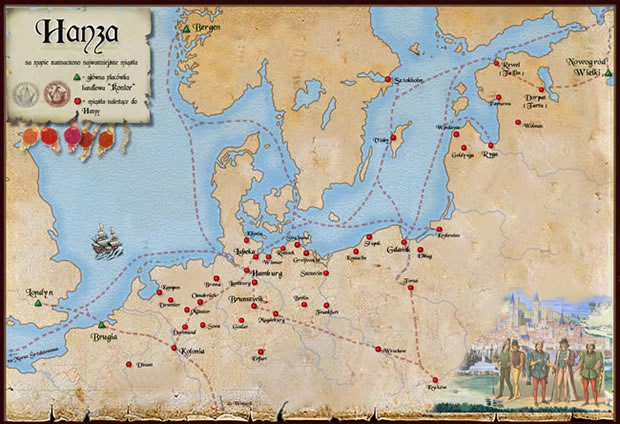
Hanseatic League
Veliky Nowogorod (Great Nowgorod) was already in the medieval kingdom of Kievan Rus' a flourishing commercial and cultural metropolis with tens of thousands of inhabitants. Novgorod hadn't never suffered of Mongols raids of Genghis Khan and temporarily it was the center of the Russian principalities and the seat of the Dukes.
Novgorod in the late Middle Ages was a city-state with good contacts to the Hanseatic League, which operated there one of its four offices.
For a long time Novgorod was struggling with the emerging Grand principality of Moscow. This rivalry ended in 1478 with the victory of Moscow over Novgorod.
1 Kievan Rus' = medieval state born in the 9th century, dominated by the city of Kiev, that now includes the territory West Russia, Belarus and West Ukraine;
2 Hanseatic League = alliance of trading cities and their guilds that established and maintained trade monopoly along the coast of Northern Europe, from the Baltic to the North Sea and inland, during the Late Middle Ages and Early modern period (c. 13th–17th centuries).




